The Role of Smart Contracts in the Crypto Ecosystem
- Understanding Smart Contracts and their Functionality
- Benefits of Using Smart Contracts in the Crypto Ecosystem
- Challenges and Limitations of Smart Contracts
- Smart Contracts vs Traditional Contracts: A Comparison
- Real-World Applications of Smart Contracts
- The Future of Smart Contracts in the Crypto Ecosystem
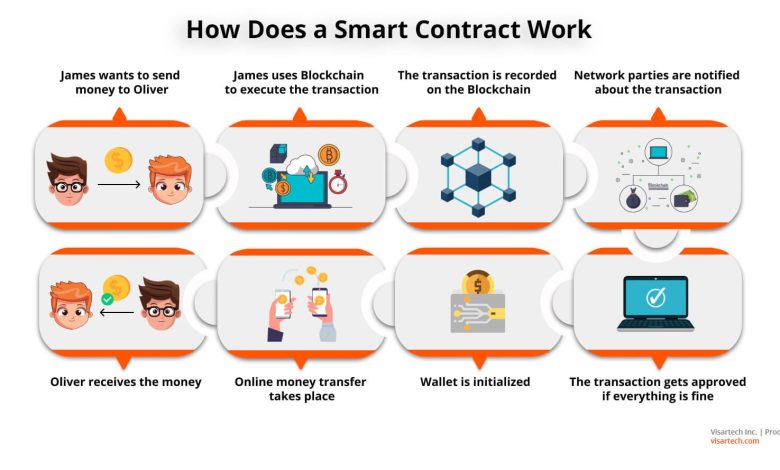
Understanding Smart Contracts and their Functionality
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. They run on the blockchain, ensuring that transactions are secure, transparent, and irreversible. These contracts eliminate the need for intermediaries, reducing costs and increasing efficiency in various industries.
Smart contracts function by automatically enforcing the terms of an agreement once certain conditions are met. They are triggered by predefined rules and execute actions accordingly. This automation streamlines processes, minimizes errors, and enhances trust among parties involved in a transaction.
One of the key features of smart contracts is their ability to facilitate complex transactions without the need for human intervention. They can be used for a wide range of applications, including supply chain management, real estate transactions, and decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols.
Benefits of Using Smart Contracts in the Crypto Ecosystem
Smart contracts offer numerous benefits to the crypto ecosystem, making them a valuable tool for users and developers alike. One of the key advantages of smart contracts is their ability to automate processes, reducing the need for manual intervention and streamlining transactions. This automation not only saves time but also minimizes the risk of human error, ensuring greater accuracy and efficiency.
Another benefit of smart contracts is their transparency. Because smart contracts are stored on a blockchain, they are visible to all parties involved in a transaction. This transparency helps to build trust among users and eliminates the need for intermediaries, reducing costs and increasing security.
Smart contracts also offer increased security through their cryptographic nature. Once a smart contract is deployed, it cannot be altered, providing a high level of protection against fraud and tampering. This security feature is particularly important in the crypto ecosystem, where trust is paramount.
Furthermore, smart contracts enable the execution of complex transactions without the need for third parties. This decentralization not only reduces costs but also increases the speed of transactions, making them more efficient and cost-effective. By eliminating intermediaries, smart contracts empower users to have more control over their assets and transactions.
Challenges and Limitations of Smart Contracts
Smart contracts have revolutionized the way transactions are conducted in the crypto ecosystem, offering increased security, transparency, and efficiency. However, like any technology, they come with their own set of challenges and limitations that need to be addressed.
One of the main challenges of smart contracts is their complexity. Writing and deploying a smart contract requires a deep understanding of programming languages and blockchain technology, which can be a barrier for many users. This complexity can also lead to errors in the code, which can result in vulnerabilities and security breaches.
Another limitation of smart contracts is their lack of flexibility. Once a smart contract is deployed on the blockchain, it cannot be easily modified or updated. This can be problematic if there are bugs in the code or if the terms of the contract need to be changed. In some cases, this inflexibility can lead to disputes between parties.
Scalability is also a concern when it comes to smart contracts. As the number of transactions on the blockchain increases, the network can become congested, leading to delays and higher fees. This can make it difficult for smart contracts to handle a large volume of transactions efficiently.
Finally, one of the biggest challenges facing smart contracts is the issue of legal enforceability. While smart contracts are designed to be self-executing and tamper-proof, there are still legal questions surrounding their validity in traditional legal systems. This lack of legal clarity can make it difficult to enforce smart contracts in case of disputes.
Smart Contracts vs Traditional Contracts: A Comparison
When comparing smart contracts to traditional contracts, it is important to understand the key differences between the two. Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. On the other hand, traditional contracts are written in natural language and require manual enforcement.
One of the main advantages of smart contracts is their automation capabilities. Once the conditions of the contract are met, the smart contract automatically executes the terms without the need for intermediaries. This not only reduces the risk of fraud but also speeds up the process significantly.
Another key difference is the level of security provided by smart contracts. Since they are stored on a decentralized blockchain network, they are tamper-proof and resistant to hacking. This provides a higher level of trust and transparency compared to traditional contracts, which are susceptible to human error and manipulation.
Additionally, smart contracts are more cost-effective as they eliminate the need for intermediaries such as lawyers or notaries. This can result in significant savings for businesses and individuals alike. Furthermore, smart contracts can be easily customized to suit specific needs, making them a versatile option for a wide range of applications.
Overall, while traditional contracts have been the norm for centuries, smart contracts offer a more efficient, secure, and cost-effective alternative. As the crypto ecosystem continues to evolve, smart contracts are likely to play an increasingly important role in shaping the future of contracts and agreements.
Real-World Applications of Smart Contracts
Smart contracts have a wide range of real-world applications that extend beyond the realm of cryptocurrencies. These applications leverage the decentralized and automated nature of smart contracts to streamline processes, reduce costs, and increase efficiency. Some of the key real-world applications of smart contracts include:
- Supply chain management: Smart contracts can be used to track and verify the authenticity of products as they move through the supply chain. This can help prevent counterfeiting and ensure that products are sourced ethically.
- Real estate transactions: Smart contracts can automate the process of buying, selling, and renting properties. This can help reduce the need for intermediaries and speed up the transaction process.
- Insurance claims processing: Smart contracts can automate the verification and processing of insurance claims, reducing the time and cost associated with manual processing.
- Legal agreements: Smart contracts can be used to create and enforce legal agreements, such as wills and contracts. This can help ensure that agreements are executed as intended and reduce the risk of disputes.
- Crowdfunding: Smart contracts can be used to automate the distribution of funds in crowdfunding campaigns, ensuring that funds are released only when certain conditions are met.
Overall, smart contracts have the potential to revolutionize many industries by automating processes, reducing costs, and increasing transparency. As the technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see even more innovative applications of smart contracts in the future.
The Future of Smart Contracts in the Crypto Ecosystem
Smart contracts are poised to play a crucial role in the future of the crypto ecosystem. These self-executing contracts are built on blockchain technology, enabling trustless and secure transactions without the need for intermediaries. As the adoption of cryptocurrencies continues to grow, smart contracts offer a way to automate and streamline various processes, from simple transactions to complex agreements.
One of the key advantages of smart contracts is their ability to eliminate the need for third parties, reducing costs and increasing efficiency. By cutting out intermediaries, smart contracts can help to speed up transactions and reduce the risk of fraud. This makes them an attractive option for a wide range of industries, from finance to real estate to supply chain management.
Looking ahead, the future of smart contracts in the crypto ecosystem looks promising. As blockchain technology continues to evolve and mature, we can expect to see even more innovative use cases for smart contracts. From decentralized finance (DeFi) to non-fungible tokens (NFTs), smart contracts are likely to play a central role in shaping the future of the digital economy.



