How Blockchain Technology Works: A Beginner’s Guide
- Understanding the basics of blockchain technology
- Exploring the key components of a blockchain
- The role of cryptography in securing blockchain transactions
- How blockchain achieves decentralization and transparency
- The process of adding new blocks to the blockchain
- Real-world applications of blockchain technology
Understanding the basics of blockchain technology
Blockchain technology is a decentralized, distributed ledger system that records transactions across multiple computers in a secure and transparent manner. The basic concept of blockchain involves a chain of blocks, where each block contains a list of transactions. These blocks are linked together using cryptographic hashes, creating a secure and tamper-proof record of all transactions.
One of the key features of blockchain technology is its transparency. All transactions on the blockchain are visible to all participants, providing a high level of accountability and trust. This transparency also helps to prevent fraud and corruption, as any unauthorized changes to the blockchain would be immediately detected by the network.
Another important aspect of blockchain technology is its security. The use of cryptographic algorithms ensures that transactions on the blockchain are secure and cannot be altered once they have been recorded. This makes blockchain technology ideal for applications where data integrity is crucial, such as financial transactions or supply chain management.
In addition to transparency and security, blockchain technology also offers increased efficiency and cost savings. By eliminating the need for intermediaries and streamlining the verification process, blockchain can help to reduce transaction times and costs. This can be particularly beneficial for industries that rely on complex supply chains or involve multiple parties.
Overall, blockchain technology has the potential to revolutionize the way we conduct transactions and manage data. By providing a secure, transparent, and efficient way to record and verify transactions, blockchain technology offers a new paradigm for trust and accountability in the digital age.
Exploring the key components of a blockchain
Blockchain technology consists of several key components that work together to create a secure and decentralized system for recording transactions. These components include:
– **Blocks**: Blocks are the individual units of data that are stored on a blockchain. Each block contains a list of transactions, a timestamp, and a unique identifier called a hash.
– **Hashes**: Hashes are cryptographic codes that are generated by running the data in a block through a mathematical algorithm. Each block’s hash is unique and is used to link it to the previous block in the chain.
– **Decentralized network**: Blockchain operates on a decentralized network of computers, known as nodes, that work together to validate and record transactions. This network ensures that there is no single point of failure and that the system is resistant to tampering.
– **Consensus mechanism**: The consensus mechanism is the protocol that determines how decisions are made on the blockchain. It ensures that all nodes in the network agree on the validity of transactions and helps prevent fraud.
– **Smart contracts**: Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. They automatically enforce the terms of the contract and can be used to facilitate a wide range of transactions.
By understanding these key components of blockchain technology, you can gain a better grasp of how this innovative technology works and its potential applications across various industries.
The role of cryptography in securing blockchain transactions
Cryptography plays a crucial role in ensuring the security of blockchain transactions. By utilizing complex mathematical algorithms, cryptography helps to encrypt transaction data, making it virtually impossible for unauthorized parties to access or alter the information. This encryption process ensures that transactions on the blockchain are secure and tamper-proof.
One of the key cryptographic techniques used in blockchain technology is hashing. Hashing involves taking an input (such as transaction data) and running it through a cryptographic hash function to produce a fixed-length string of characters, known as a hash. This hash uniquely represents the original input data and is used to verify the integrity of the information stored on the blockchain.
Another important cryptographic tool used in blockchain technology is digital signatures. Digital signatures are created using a combination of public and private keys, where the private key is used to sign a transaction and the public key is used to verify the signature. This process ensures that transactions are authentic and have not been tampered with by malicious actors.
Overall, cryptography plays a vital role in securing blockchain transactions by providing encryption, hashing, and digital signature mechanisms to protect the integrity and confidentiality of data on the blockchain. By leveraging these cryptographic techniques, blockchain technology can offer a high level of security and trust in the digital world.
How blockchain achieves decentralization and transparency
Blockchain technology achieves decentralization and transparency through its unique design and consensus mechanisms. By utilizing a distributed network of nodes, blockchain ensures that no single entity has control over the entire system. This decentralized nature of blockchain helps in preventing fraud, manipulation, and censorship, as there is no central point of failure.
Transparency is another key feature of blockchain technology. Every transaction that occurs on a blockchain is recorded in a public ledger that is accessible to all participants in the network. This transparency helps in building trust among users, as they can verify the authenticity of transactions without relying on intermediaries. Additionally, the immutability of blockchain ensures that once a transaction is recorded, it cannot be altered or deleted, further enhancing transparency.
The consensus mechanisms used in blockchain, such as Proof of Work (PoW) or Proof of Stake (PoS), play a crucial role in maintaining decentralization and transparency. These mechanisms ensure that all participants in the network agree on the validity of transactions and the order in which they are added to the blockchain. This agreement is reached through a process of validation and verification, which helps in preventing double-spending and other fraudulent activities.
Overall, blockchain technology’s decentralized and transparent nature makes it a powerful tool for various industries, including finance, supply chain management, healthcare, and more. By leveraging blockchain, organizations can streamline operations, reduce costs, and enhance security while promoting trust and accountability in their processes.
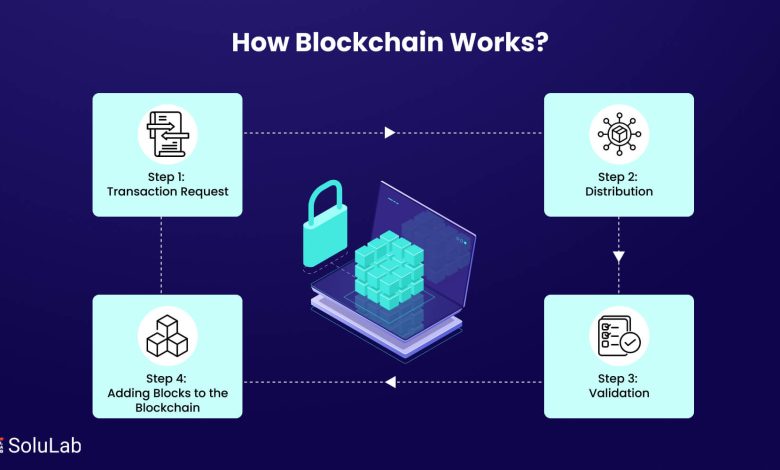
The process of adding new blocks to the blockchain
The process of adding new blocks to the blockchain involves a series of steps that ensure the security and integrity of the network. When a new transaction is initiated, it is broadcasted to all nodes in the network. These nodes then validate the transaction to ensure that it is legitimate and meets the criteria set by the consensus algorithm.
Once the transaction is validated, it is grouped with other transactions to form a new block. This block is then added to the existing blockchain through a process called mining. Miners compete to solve complex mathematical puzzles, and the first one to solve the puzzle gets to add the block to the blockchain.
Adding a new block to the blockchain requires a significant amount of computational power, which helps to secure the network against potential attacks. Once a block is added, it is linked to the previous block through a cryptographic hash function, creating a chain of blocks that cannot be altered without the consensus of the majority of nodes in the network.
Overall, the process of adding new blocks to the blockchain is essential for maintaining the decentralized and transparent nature of the technology. By following a set of predefined rules and protocols, the blockchain ensures that all transactions are secure and immutable, making it a reliable and trustworthy system for storing and transferring digital assets.
Real-world applications of blockchain technology
Blockchain technology has a wide range of real-world applications beyond just cryptocurrencies. One of the most prominent uses is in supply chain management. Companies can use blockchain to track the movement of goods from the manufacturer to the consumer, ensuring transparency and authenticity throughout the process. This helps in reducing fraud and ensuring the quality of products.
Another significant application of blockchain technology is in the healthcare industry. By storing patient records on a blockchain, medical professionals can access accurate and up-to-date information quickly and securely. This can improve the quality of care and reduce medical errors. Additionally, blockchain can be used to track the authenticity of pharmaceuticals, reducing the prevalence of counterfeit drugs in the market.
Blockchain technology is also being utilized in the voting system to ensure the integrity of elections. By recording votes on a blockchain, it becomes nearly impossible to tamper with the results, ensuring a fair and transparent electoral process. This can help in increasing voter trust and participation in democratic processes.
Furthermore, blockchain technology is revolutionizing the real estate industry by enabling transparent and secure property transactions. Smart contracts on a blockchain can automate the process of buying, selling, and renting properties, reducing the need for intermediaries and minimizing the risk of fraud.
Overall, blockchain technology has the potential to transform various industries by providing secure, transparent, and efficient solutions to complex problems. Its decentralized nature and cryptographic security make it a valuable tool for ensuring trust and authenticity in a wide range of applications.



